This type of industrial heat exchanger, which is widely used in various industries, is made of shell-tube heat exchangers with a circular cross-section, which are installed in a cylindrical shell. So that the axis of the pipes is parallel to the axis of the shell.
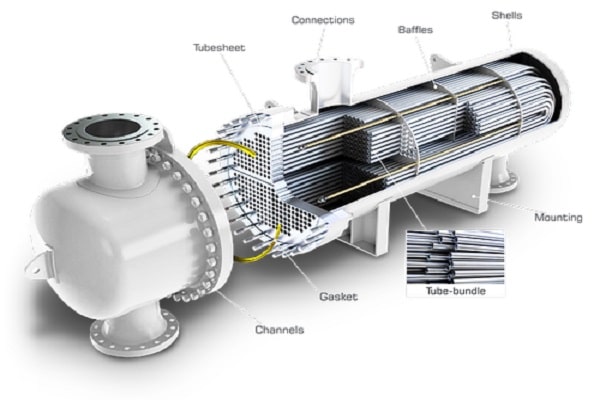
shell & tube heat exchanger
This type of industrial heat exchanger, which is widely used in various industries, is made of shell-tube heat exchangers with a circular cross-section, which are installed in a cylindrical shell. So that the axis of the pipes is parallel to the axis of the shell.
This type of industrial heat exchanger, which is widely used in various industries, is made of shell-tube heat exchangers with a circular cross-section, which are installed in a cylindrical shell. So that the axis of the pipes is parallel to the axis of the shell.
This type of converter can be used for high contact surface with pressure higher than 30 bar and temperature higher than 260 degrees Celsius. It can be said that the structure of the transducers consists of a number of pipes that are placed inside a cylinder and two desired fluids, one cold and the other hot, without directly colliding with each other through the metal wall of the pipes heat exchange with each other. They will
In other words, one of these two fluids will flow in the tubes and the other around the tubes, inside the shell. Two fluids can move in two phases and in unequal directions
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of three main parts:
- Front header: The fluid inlet part is inside the converter tubes.
- Rear header: The fluid output part of the converter is for single-pass converters and the fluid return part is the front header for multi-pass converters.
- Bundle tube: which includes tube, tube holder, baffle, tie rods and.. The shell holds the bundle tube.
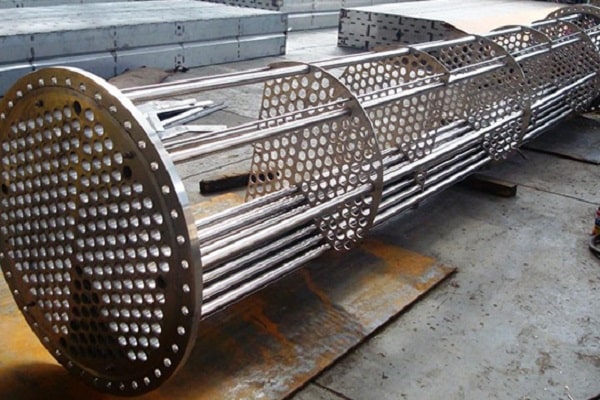

Shell and tube heat exchangers are divided into the following three categories:
- Fixed Tube Sheet Exchanger
- Converter with U-shaped pipes (U – Tube Exchanger)
- Floating Head Heat Exchanger
How to place the tubes
The choice of tube diameter is selected according to the descaling properties of the fluid, the required distance between the tubes and the cost. Typically, the outer diameter of the tubes is considered to be between 19.05 and 25.4 mm, which in small units, this outer diameter can be reduced to 6.35 mm.
The maximum tube length for heat exchangers that can remove the bundle is limited to 9 meters. The maximum tube length for fixed heat exchanger tube heat exchangers is not limited and is usually considered up to a maximum of 15 meters. Tubes can be arranged triangularly or squarely along the bundle
When mechanical cleaning is required, the tubes are arranged squarely. The triangular arrangement of the tube allows more tubes to be placed in the space along the bundle.
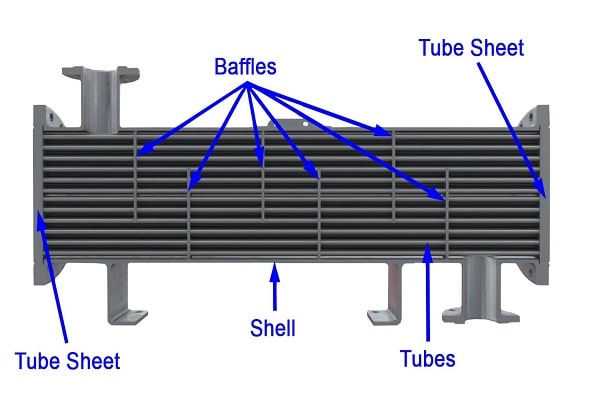
How to place the baffles
Baffles are used for two purposes. Conduct fluid and hold pipes to prevent vibration and displacement. By installing baffles, the flow of fluid in the shell is almost perpendicular to the flow of fluid inside the pipes, which increases the heat transfer and thus increases the work efficiency.
Collision plate
This plate, which is larger than the diameter of the nozzle inlet hole, is about 6 mm thick and flat or curved. This plate is installed after the nozzle inlet and before the inlet of the tubes to prevent the entry of solid objects or liquid droplets trapped on the side of the shell.
Source : sabalan weblog

https://newfasttadalafil.com/ – buy cialis online reviews Gnqfkf Elevated BUN is also seen with catabolic drugs e. daily cialis online Ztvwvl https://newfasttadalafil.com/ – cialis 10mg Hvgjbj