Filtration:
it is widely used in biotechnology to separate materials based on the relative size of particles. under pressure to liquid has different types, including:
- Microfiltration (MF)
- Ultrafiltration (UF)
- Reverse Osmosis and Nano filtration (RO/NF)
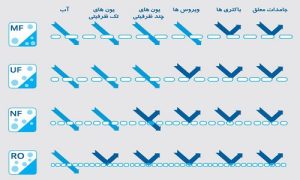
Microfiltration:
The best type of filter used in general is microfiltration, microfiltration (MF) is the creation of particles behind an environmental filter while the body suspended in it passes through the filter. Particles are retained in the filter pores because they are larger. Other factors on retention are fluid viscosity and chemical interactions between the membrane and the particles in the solution. Microfiltration removes particles with a pore size of 0.05 and 5.0 µm.
Separator of colloidal substances, polymers, suspended substances and food
- Needs low pressure difference compared to RO
- Application in water purification, dairy, food and pharmaceutical industries
Ultrafiltration:
Ultrafiltration (UF) works essentially like microfiltration, except that the pore sizes are significantly smaller. Solutes are retained behind the filter by molecular size, while most of the liquid and dissolved salts pass through. A fluid force across the membrane, known as transmembrane pressure, drives the filtration process. Ultrafiltration membranes are designed for the concentration and separation of complex protein mixtures. When water undergoes microfiltration, many microorganisms are removed, but viruses remain in the water. Ultrafiltration removes these larger particles and may remove some viruses.
- Pre-treatment of RO and NF systems and removal of SDI (fine suspended particles)
- Purification of 99.99% of microorganisms, bacteria, emulsions, petroleum substances, oil, pigments, etc.
- NTU (turbidity) of the output water is less than 0.02
- Municipal and domestic wastewater treatment
- Removal of oxygen and carbon from liquids
- Common use in various industries such as food, oil, textile, drinking water
Reverse osmosis (RO) and Nano filtration (NF):
Reverse osmosis (RO) and Nano filtration (NF) are processes for the separation of very low molecular weight molecules (less than 1500 Daltons) from solvents, often water. The main basis of separation is the removal of solutes by the membrane based on size and charge. Unlike UF membranes, RO and NF membranes retain most of the salts as well as uncharged solutes. Reverse osmosis (RO) membranes have very small pore sizes and are designed to separate ions from each other. After the water passes through the reverse osmosis filter, it is essentially pure water. In addition to removing all organic molecules and viruses, reverse osmosis also removes many of the minerals in the water, meaning it sweetens the water.
Nano filtration system:
- Application in water purification, fruit juice, and pharmaceutical and…
- Removes the hardness and reduces the color and smell of drinking water
- Purification of industrial and agricultural wastewater
- Disinfection of surface and underground water
- Reverse osmosis (RO) system pre-treatment
Reverse osmosis system:
- Ability to receive raw water input with high TDS (total hardness of water and total dissolved solids) even sea water and oceans
- The ability to separate pollutants that give the water an unpleasant color, taste and smell, such as alkaline and salty tastes created by chlorides and sulfates.
- Non-use of substances harmful to humans in this system
- Eliminating all pollutants such as organic, inorganic and microbial pollutants
-Dalton (da) unit is * 9.210-18

